The application used to replicate data for server replacements was having problems replicating all the data from the source server. It turns out, the server owner had locked down certain files and folders, excluding the account used by the replication software. This prevented the app from copying all the data.
I used AccessChk to determine offending files. This free tool can be downloaded from here:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/bb664922.aspx
I copied the exe to the server and ran the following command:
accesschk.exe -n -s MyDomain\MyAccount d:\ > c:\noaccess.txt
-n Show only objects that have no access
-s Recurse
I then piped the output to a text file called noaccess.txt.
I ran this against a Windows 2008 server. Unfortunately, there were so many offending files, it bonked out after the text file reached about 32MB..... But it gave us a place to start.
Happy Hunting.
I'm a Sr. Systems Engineer at a Global Environmental Engineering company. I've been in IT since 1999 and from 2005, my focus has been VMware datacenter products. More recently, my attention has been for Microsoft Azure services. As the Global Service Owner for VMware Datacenter products, I've had the pleasure of having in-depth and hands-on experience with not only VMware products, but server, storage and networking technologies.
Friday, August 1, 2014
Tuesday, July 29, 2014
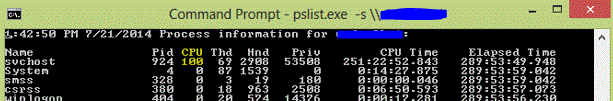
How to find the processes running on a remote server AND how to find the services associated with svchost.exe.
We had a server which was running at 100% cpu utilization. Unfortunately,
we were unable to RDP into the server to identiify the offending process.
To get the process details of a remote server, I used PsList.exe. PSList is a part of a suite of tools which can be downloaded here:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/bb896649.aspx
In this case, it was svchost.exe. Since there can be multiple svchost processes running, take note of the Process ID (Pid). svchost.exe can contain other individual services. To find out what they are, use tasklist and match up the PID to the offending service. (In this case 924)
tasklist /s myserver /svc /fi "imagename eq svchost.exe"
To get the process details of a remote server, I used PsList.exe. PSList is a part of a suite of tools which can be downloaded here:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/bb896649.aspx
In this case, it was svchost.exe. Since there can be multiple svchost processes running, take note of the Process ID (Pid). svchost.exe can contain other individual services. To find out what they are, use tasklist and match up the PID to the offending service. (In this case 924)
tasklist /s myserver /svc /fi "imagename eq svchost.exe"
Wednesday, June 25, 2014
Quick Tip: Faster way of logging into a server using a local account
I was working with a co-worker and noticed he was logging into a w2k8r2 server using a local account and typing in the entire server name and user account.
Instead of typing in the local server name just use the following:
.\
Faster, simpler and more accurate!
Instead of typing in the local server name just use the following:
.\
Faster, simpler and more accurate!
Wednesday, June 18, 2014
Powershell fix: The trust relationship between this workstation and the primary domain failed
We're a heavily virtualized shop. To save on host resources, we often shutdown Test/Dev/Staging/template servers that are not in use.
One of the drawbacks of this is I would often receive the following error when powering on a server that has been off the network for a while:
The error is often due to the computer password no longer matching the one in Active Directory. This is caused by the computer being offline for a while, or when reverting to an old snapshot or backup.
In the past, I've been removing the server from AD and rejoining the domain. As the number of these occurances have increased, I've been leveraging powershell to fix this issue as quickly and efficiently as possible.
To resolve this issue, log into the offending server using the local admin account. Launch Powershell as an administrator and run the following cmdlet:
Reset-ComputerMachinePassword [-Credential <PSCredential> ] [-Server <String> ] [-Confirm] [-WhatIf] [ <CommonParameters>]
For -server, enter your the domain controller.
Enter the password when prompted and reboot. You will now be able to log into the server using domain credentials.
**Update**
If you're using a version of powershell below 3, you'll receive the following error:
Reset-ComputerMachinePassword : A parameter cannot be found that matches parameter name 'credential'.
In that case, I typically fall back to the old Netdom command:
netdom resetpwd /s:server /ud:domain\User /pd:*
or
netdom resetpwd /server:server /userD:domain\User /PasswordD *
One of the drawbacks of this is I would often receive the following error when powering on a server that has been off the network for a while:
The error is often due to the computer password no longer matching the one in Active Directory. This is caused by the computer being offline for a while, or when reverting to an old snapshot or backup.
In the past, I've been removing the server from AD and rejoining the domain. As the number of these occurances have increased, I've been leveraging powershell to fix this issue as quickly and efficiently as possible.
To resolve this issue, log into the offending server using the local admin account. Launch Powershell as an administrator and run the following cmdlet:
Reset-ComputerMachinePassword [-Credential <PSCredential> ] [-Server <String> ] [-Confirm] [-WhatIf] [ <CommonParameters>]
For -server, enter your the domain controller.
Enter the password when prompted and reboot. You will now be able to log into the server using domain credentials.
**Update**
If you're using a version of powershell below 3, you'll receive the following error:
Reset-ComputerMachinePassword : A parameter cannot be found that matches parameter name 'credential'.
In that case, I typically fall back to the old Netdom command:
netdom resetpwd /s:server /ud:domain\User /pd:*
or
netdom resetpwd /server:server /userD:domain\User /PasswordD *
Tuesday, June 3, 2014
Security Warning - Run only scripts that you trust.
Ok, I'm embarrassed about this one... I was receiving the following prompt and it took me a sec to sort this one out.
To disable the above warning, perform one of the following:
1. Unblock the file through the GUI:
1. Unblock the file through the GUI:
2. Use the Powershell unblock-file cmdlet
Done!
How to schedule PowerShell Scripts with Parameters
The global VMware admins at the company I work at needed a mechanism to monitor the membership of AD groups associated with the virtual environment.
The following script by Francois-Xavier Cat fit the bill perfectly! (Thanks again!)
http://www.lazywinadmin.com/2013/10/powershell-monitor-and-report-active.html
Setup was simple and it ran perfectly in the Powershell ISE. However, when it came time to scheduling it in Windows Task Scheduler, I had a bit of trouble. It turn out, escape characters (ex. \) are needed for it to run properly.
In the Program/script field enter the following:
C:\Windows\system32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe
In the Add arguments field, the following was entered:
-command "D:\MyFolder\TOOL-MONITOR-AD_Group_20131127.ps1 -group \"group01\",\"group02\",\"group03\" -EmailFrom test@MyDomain.com -Emailto \"user01@MyDomain.com\",\"user02@MyDomain.com\",\"user03@MyDomain.com\" -emailserver smtprelay.MyDomain.com
The following script by Francois-Xavier Cat fit the bill perfectly! (Thanks again!)
http://www.lazywinadmin.com/2013/10/powershell-monitor-and-report-active.html
Setup was simple and it ran perfectly in the Powershell ISE. However, when it came time to scheduling it in Windows Task Scheduler, I had a bit of trouble. It turn out, escape characters (ex. \) are needed for it to run properly.
In the Program/script field enter the following:
C:\Windows\system32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe
In the Add arguments field, the following was entered:
-command "D:\MyFolder\TOOL-MONITOR-AD_Group_20131127.ps1 -group \"group01\",\"group02\",\"group03\" -EmailFrom test@MyDomain.com -Emailto \"user01@MyDomain.com\",\"user02@MyDomain.com\",\"user03@MyDomain.com\" -emailserver smtprelay.MyDomain.com
Tuesday, May 20, 2014
Powershell: Verifying the vCenter Services are running
This past weekend, I was unable to log into our vCenter server. To quickly get the status of vCenter Services, I ran the following commands.
get-service -cn YourvCenterServer -DisplayName VMware*
Unfortunately, the vCenter SSO service has a different service naming convention (gsv is an alias for get-service):
gsv -cn YourvCenterServer -DisplayName vCenter*
It turns out, the volumes associated with the sql server housing the vCenter DB were being moved from the Equallogic to the Compellent array....
get-service -cn YourvCenterServer -DisplayName VMware*
Unfortunately, the vCenter SSO service has a different service naming convention (gsv is an alias for get-service):
gsv -cn YourvCenterServer -DisplayName vCenter*
It turns out, the volumes associated with the sql server housing the vCenter DB were being moved from the Equallogic to the Compellent array....
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)